 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
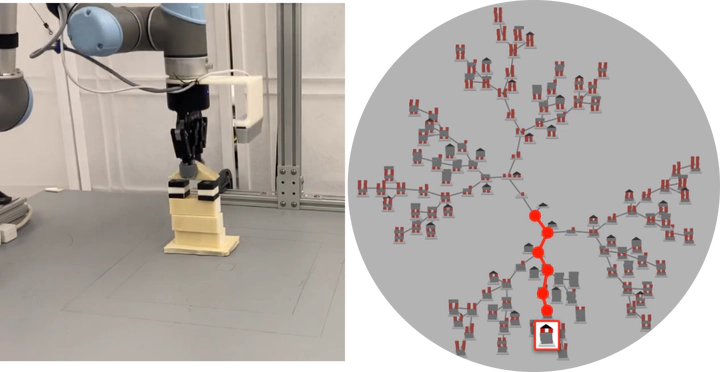
Multi-goal policy learning for robotic manipulation is challenging. Prior successes have used state-based representations of the objects or provided demonstration data to facilitate learning. In this paper, by hand-coding a high-level discrete representation of the domain, we show that policies to reach dozens of goals can be learned with a single network using Q-learning from pixels. The agent focuses learning on simpler, local policies which are sequenced together by planning in the abstract space. We compare our method against standard multi-goal RL baselines, as well as other methods that leverage the discrete representation, on a challenging block construction domain. We find that our method can build more than a hundred different block structures, and demonstrate forward transfer to structures with novel objects. Lastly, we deploy the policy learned in simulation on a real robot.